
Why students should focus more on recall instead of writing notes
Active recall is a better way to study compared to writing notes. Here’s why:
- Note-taking issues: Students often write down only one-third of key points, leading to poor retention and a shallow understanding.
- Active recall benefits: It strengthens memory by retrieving information from your brain, not just reviewing notes. This method improves long-term retention and helps identify knowledge gaps.
- How to use active recall: Test yourself, summarize from memory, or use flashcards. Combine this with spaced repetition for better results.
Quick Comparison:
| Aspect | Note-Taking | Active Recall |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Style | Passive | Active |
| Retention Over Time | Low | High |
| Engagement Level | Surface-level processing | Deep memory engagement |
| Study Outcome | False sense of knowledge | Real understanding |
Switching to active recall can significantly improve learning efficiency and memory retention.
Research on Active Recall
What Active Recall Means
Active recall is a learning technique where you actively retrieve information from memory instead of just reviewing it passively . Unlike simply copying notes word-for-word, active recall pushes you to mentally retrieve information, which, according to brain scans, activates deeper memory networks . This sets the stage for research that confirms its effectiveness.
Research Results
A meta-analysis highlights active recall as one of the most effective study techniques . Psychologist William James once remarked:
"A curious peculiarity of our memory is that things are impressed better by active than by passive repetition... it pays better to wait and recollect by an effort from within, than to look at the book again."
Modern brain imaging backs this up, showing that active recall not only strengthens memory but also helps identify gaps in knowledge.
Active vs. Passive Study Methods
Here’s how active recall measures up against passive review and basic note-taking:
| Study Method | Memory Engagement | Immediate Recall | Retention | Learning Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active Recall | Deep neural networks | Moderate | Very High | High |
| Passive Review | Shallow neural networks | High | Low | Low |
| Note-Taking | Surface-level processing | Moderate | Low | Low |
C. A. Mace's research supports these findings:
"Active repetition is very much more effective than passive repetition... when acts of reading and acts of recall alternate... the efficiency of learning and retention is enormously enhanced."
Additionally, active recall promotes "across-episode binding", a process where new information connects with what you already know . This strengthens your understanding and makes learning more impactful.
How to Use Active Recall
Self-Testing Methods
Active recall is a powerful way to learn effectively. Start by jotting down everything you can remember about a topic on a blank sheet of paper - this helps identify gaps and strengthens your understanding . Before diving into new material, try testing yourself on it. This primes your brain for quicker learning . Another helpful tactic? Explain the material out loud, even if it's just to an empty room. This process makes concepts clearer and easier to retain . To stay organized, use flashcards as a tool for structured practice.
Flashcard Best Practices
Well-designed flashcards can make a big difference in your study sessions. Here are some tips to maximize their effectiveness:
| Aspect | Best Practice | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Content Focus | Stick to one concept per card | Helps form clear and strong memories |
| Question Format | Use precise prompts with one answer | Avoids confusion and improves recall |
| Visual Elements | Add diagrams or images when relevant | Activates multiple memory pathways |
| Organization | Group related ideas together | Encourages logical connections |
You can also try techniques like cloze deletions (filling in blanks) or image occlusion (hiding parts of an image) to stay engaged . Pair these strategies with a spaced review schedule to keep your learning on track.
Spaced Review Schedule
A solid review plan can work wonders for memory retention. Dominic O'Brien, a world memory champion, suggests reviewing material at specific intervals: right after learning, then 24 hours later, followed by one week, one month, and three months .
Digital tools like Anki can simplify this process by using algorithms to adjust review timing based on how well you're doing . If you answer correctly, the time between reviews increases; if you struggle, the system schedules more frequent reviews .
The Pimsleur method also highlights the value of spaced intervals (immediate, 24 hours, one week, one month, etc.) for reinforcing knowledge without spending too much time . Even partial recall during these reviews helps solidify information over the long term . The trick is to stick to a consistent schedule and adjust based on how challenging the material is for you.
How to Study & Learn Using Active Recall
Digital Tools for Active Recall
Active recall is a proven way to strengthen memory, and now digital tools make it easier than ever to incorporate this technique into your study routine.
Anki and Quizlet Features

Tools like Anki and Quizlet use digital flashcards and spaced repetition to support active recall. Anki's FSRS algorithm prioritizes tougher material for review, ensuring you focus on what needs the most attention .
Quizlet offers various study modes tailored to different learning needs:
| Study Mode | Purpose | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Flashcards | Quick review | Beginners |
| Learn | Adaptive questioning | Building confidence |
| Write | Written responses | Deep understanding |
| Spell | Audio-based learning | Language practice |
| Test | Mixed-format quizzes | Self-assessment |
These platforms are versatile, but other tools provide even more advanced features for active recall.
intellecs.ai Study Tools
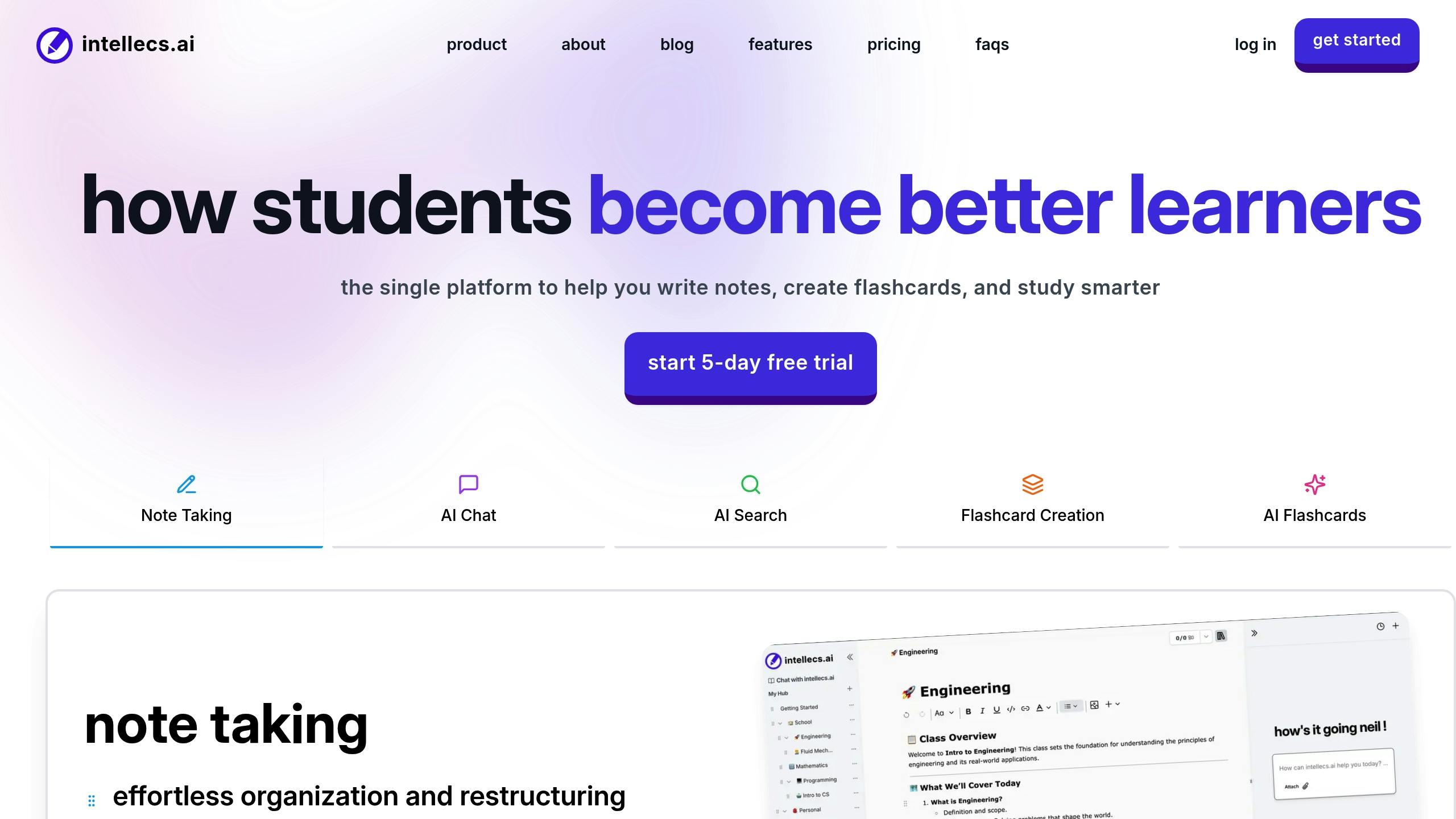
Intellecs.ai takes active recall to the next level with AI-generated flashcards, organized notes featuring built-in recall prompts, and context-aware resource searches. For $25 per month, users gain unlimited access to these features, making it a convenient all-in-one solution for students aiming to streamline their study process .
Combining Digital Notes with Active Recall
Enhance your learning by pairing digital flashcards with active recall techniques in your note-taking. Digitize your notes and turn essential points into flashcards. Add handwritten notes or visuals for complex topics, and let spaced repetition tools handle the review schedule . To fully grasp challenging concepts, choose tools that support multimedia elements, such as images and diagrams, to deepen your understanding .
Switching to Active Recall
Active recall is a powerful technique for improving memory retention. Here's how you can shift from passive note-taking to actively engaging with your study material.
Step-by-Step Transition Plan
Use a phased approach to ease into active recall. Start with one subject to build the habit.
| Phase | Duration | Activities | Goal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Week 1-2 | Read and take basic notes | Understand the material |
| Integration | Week 3-4 | Turn notes into questions | Begin practicing retrieval |
| Mastery | Week 5+ | Fully use active recall | Strengthen memory connections |
This method helps you gradually incorporate active recall into your study routine.
Turning Notes into Recall Prompts
Here’s how to make your notes work harder for you:
- Convert statements into questions: For example, instead of listing the parts of photosynthesis, ask, "What are the three elements required for photosynthesis?"
- Summarize from memory: After each study session, write a summary of key concepts without looking at your notes. This helps identify gaps in your understanding and reinforces learning .
"Active recall is all about retrieving information from your memory during the learning process, rather than simply consuming information passively. As you'll learn, it's not just what you study, but how you study." - Dom, Founder of Traverse
Tackling Common Challenges
Active recall can be tough, and that's a good thing. Here’s how to deal with common obstacles:
- Mental Fatigue: Take short breaks between sessions to stay focused. Remember, the harder it feels, the more effective it is .
- Knowledge Gaps: Spend at least 30 seconds trying to answer a question before checking your notes. This strengthens memory connections .
"Active recall is challenging; it should feel tough; that is where the real learning happens. Make sure you are working your brain and attempting answers before showing yourself the answer to questions." - Zach Highley
Conclusion
Active recall boosts learning in a big way. Studies show it's 51% more effective than passive review. For instance, testing yourself once can outperform reading a chapter four times .
This method works by strengthening neural pathways and moving information from short-term to long-term memory . Digital tools like Anki and intellecs.ai make it easier by automating spaced repetition and providing AI-powered flashcards.
Struggling with active recall? That’s a good sign - it means real learning is happening. In one study, participants using active recall remembered almost twice as much: 57% compared to 29% for those who stuck to passive reading . These results highlight the need for smarter study methods.
Switching from traditional note-taking to active recall can change how you study. Pairing strategic notes with active recall techniques helps students build habits that lead to lasting academic success.